The Bible - Old Testament
Abraham [Migrated from Haran, Mesopotamia (1:12:4) to Canaan]
Abraham's sons: Ishmael (son of Hagar, servant of Sarah 1:16:1) and Isaac (son of Sarah 1:21:1)
One (of two) of the more influential attempts to match biblical chronology to historical dates, places Abraham's life between 1812 and 1637 BCE., but within the biblical text itself there are problems with it's historicity. Some events narrated in the story could not have occurred before the 12th century BCE. -- Wikipedia -- Historicity and origins
 sons of Isaac: Esau and Jacob Israel -
sons of Isaac: Esau and Jacob Israel -
sons of Jacob:
sons of Leah: Reuben, Simeon, Levi, Judah;
sons of Biliah, Rachel's maidservent: Dan and Naphtali;
sons of Zilipah, Leah's maidservent: Gad and Asher;
sons of Leah: Issachar, Zebulun;
sons of Rachel: Joseph and Benjamin
Because of famine late in the life of Jacob, the family moved, at the behest of Joseph, to Egypt. For a time the Israelites prospered in Egypt but with a change of pharaohs the Israelites lost their standing and became enslaved.
In the time of Moses, son of Amram, son of Kohath son of Levi, the Israelites returned to Canaan.
Rabbinical Judaism calculated a lifespan of Moses corresponding to 1391–1271 BCE. The tradition of Moses as a lawgiver and culture hero of the Israelites can be traced to the 8th or 7th century BCE in the kingdom of Judah.
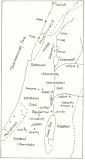
After the conquest of Canaan by Joshua (following the death of Moses), the tribes of Israel lived as a confederation governed by leaders called Judges. Saul from the tribe of Benjamin was annointed by Samuel as the first King of Israel, but it was
David of the House of Judah who created a strong unified Israelite monarchy - c. 1040–970 BCE,
king of Judah c. 1010–1002 BCE; king of the United Kingdom c. 1002–970 BCE.
Following the death of Solomon, son of David, the united Israel split into two kingdoms: the northern Kingdom of Israel and the southern Kingdom of Judah.
-- Genealogy of the Kings of Israel and Judah
Omri, Ahab, Ahaziah and Jehoram
Vilified in the Bible, little attention is paid to Omri (c.876 BCE) aside from noting the establishment of the
Omrides Dynasty, the foundation of Samaria as Israel's new capital (c.876-837 BCE), and colorful stories of
King
Ahab and his wife Jezebel.
Israel Finkelstein and Asher Silberman argue archeological sites attributed to King Solomon and the united kingdom, based solely upon on Biblical texts, actually belong to the later period of the Omri Dynasty (Omri - Ahab c.871 – c.850 BCE). Finkelstein and Silberman's work is based in archeology and supported by extra-Biblical texts. -- The Bilble Unearthed.
Ancient Israel: BCE 1200 - BCE 722.
E Text BCE 922 - BCE 722 -- Israel, 'Elohim' Text
J Text BCE 848 - BCE 722 -- Judah, 'Yahweh' Text
Both texts written before the Assyrians (Tiglath-pileser III
/Shalmanesser V) destroyed Israel (c. BCE 722). Refugees fled south to Judah and both texts were merged.
-- Richard Elliot Friedman - 'Who Wrote the Bible'
Hezekiah, Manasseh, Amon, Josiah
Hezekiah: (14th king of Judah) 715-687 BCE. Religious and political reformer. Hezekiah rejected Assyrian's suzerainty.
In 701 BCE, Sennacherib turned from Babylonia to the western part of the empire, where Hezekiah of Judah, incited by Egypt and Marduk-apla-iddina, had renounced Assyrian allegiance. The rebellion involved various small states in the area: Sidon and Ashkelon were taken by force and a string of other cities and states, including Byblos, Ashdod, Ammon, Moab and Edom then paid tribute without resistance. Ekron called on Egypt for help but the Egyptians were defeated. Sennacherib then turned on Jerusalem, Hezekiah's capital. He besieged the city and gave its surrounding towns to Assyrian vassal rulers in Ekron, Gaza and Ashdod. Sennacherib however never breached the city. Hezekiah remained on his throne as a vassal ruler (The campaign is recorded with differences in the Assyrian records and in the biblical Books of Kings). -- Wikipedia
Josiah, King of Judah (reign 641-609 BCE), son of King Amon.
His grandfather, Manasseh was one of the kings blamed for turning away from the worship of YHWH. At the start of Josiah's reign the Assyrian Empire was beginning to disintegrate, Egypt to the west was still recovering from Assyrian rule, and the Babylonian Empire had not yet risen. Josiah returned to the reformations established by his great-grandfather (Hezekiah) and Jerusalem was able to govern itself without foreign intervention.
Early in the reign of Josiah money was used to renovate the temple, and during those repairs the high priest Hikiah found 'the Book of Law' in the house of Jehovah (12:22:4). Since before the 5th century Biblical scholars (such as Jerome) have insisted that the text found by Hilkiah was the law code of Deuteronomy. Other scholars suggest the text was written at Josiah's instigation and "found" to justify his reformations.
The Deuteronomistic History written (or certainly edited) during the reign of Josiah, along with the following six books: Joshua, Judges, Samuel and Kings. The author/editor was a Levite priest 609-587 BCE, possibly Baruch son of Neriyah, scribe to Jeremiah.
Egypt supported Assyria against the potential threat of the Medes and the Babylonians:
While Josiah was king, Pharaoh Necho king of Egypt went up to the Euphrates River to help the king of Assyria. King Josiah marched out to meet him in battle, but Necho faced him and killed him at Megiddo. -- 2 Kings 23:29
Necho replaced Josiah’s chosen successor with his own nominee and imposed tribute on Judah. In 606 the Egyptians routed the Neo-Babylonians, but at the great Battle of Carchemish (a Syrian city on the middle Euphrates River) in 605 the Neo-Babylonian crown prince, Nebuchadrezzar, soundly defeated Necho’s troops and forced their withdrawal from Syria and Palestine.
[Jeremiah's ministy spanned the time period of the 13th year of Josiah (BCE 626) until sometime after the fall of Jerusalem and destruction of Solomon's Temple in 587 BCE. His prophetic work spanned the reigns of five kings of Judah: Josiah, Jehoahaz, Jehoiakim, Jehoichin and Zedekiah. After Jeremiah prophesied that Jerusalem would be handed over to the Babylonian army, the king's officials imprisoned him until Jerusalem fell to the Babylonian army in 587 BCE. The Babylonians released Jeremiah, allowing him to choose the place of his residence. Jeremiah accordingly went to Mizpah in Benjamin with Gedaliah, who had been made governor of Judea. Johanan succeeded Gedaliah, and later fled to Egypt, taking with him Jeremiah and Baruch, Jeremiah's faithful scribe and servant.]
Nebuchadnezzar c.634 - 562 BCE Akkadian name, Neabu-kudurri-usur - Oh god Nabu preserve my first born son. Nabu is the Babylonian deity of wisdom and son of Marduk. Nebuchadnezzar delivered Babylon from its dependence on Assyria and laid Nineveh in ruins. He engaged in several military campaigns designed to increase Babylonian influence in Syria and Judah. An attempted invasion of Egypt in 601 BCE was met with setbacks, however, leading to numerous rebellions among the states of the Levant, including Judah. Nebuchadnezzar captured Jersusalem in 597 BCE and deposed Jehoiakim, destroying both the city and temple, and deporting many of the prominent citizens along with a sizable portion of the Jewish population of Judea to Babylon. -- Wikipedia
Siege of Jerusalem of 597 (BCE)
[Daniel belongs to the end of the First Temple Period and was taken in captivity to Babylon by Nebuchadnezzar. A young noble of Jerusalem birth, he is said to have served Nebuchadnezzar and his successors with loyalty and ability until the time of the Persian conquerer Cyrus, all the while remaining true to the God of Israel.]
The Priestly source - written during or after the exile, c.550-400 BCE
In B.C. 538 the Persians conquered the Babylonians - Babylonia, Egypt and everything in between, including Judah.
Cyrus the Great allowed the Jews to return to Judah.
The second temple stood between 516 BCE and 70 CE.
Ezra, The 'redactor', sent to Jerusalem by the Persian King Artaxerxes, c.465-424 BCE -or- 404-359 BCE.
Nehemiah - governor of Judah under King Artaxerxes
The Books of Chronicles c. 400 - 250 BCE (350–300 BCE).
Early Roman Emperors --
| Augustus | | 27 BC - 14 AD |
| Tiberius | | 14 AD - 37 AD |
| Caligula | | 37 AD - 41 AD |
| Claudius | | 41 AD - 54 AD |
| Nero | | 54 AD - 68 AD |
The second temple period ended with the First Jewish-Roman War (66 - 73 CE)
Bar Kokhba revolt 132-136 CE.
Old Testament Sources and other traditions:
Haggadah: Legend. Oral tradition of stories.
Pentateuch or Torah: Five Scrolls or Instruction
Talmud: Vast collection of the Jewish writings completed from the post biblical period of the fourth century of the Common Era for the Palestinian Talmud, and the fifth and sixth century CE for the Babylonian Talmud.
Mishnah. The Hebrew text of the Talmud.
Gemara: The Aramaic commentary in the Talmud.
Midrash: Jewish commentaries on the Bible written between Exile and c. 1200 CE
Links:
Israelites
Ten Lost Tribes
History of Israel and Judah
Genealogy of Jesus
Black Book > Biblical Old Testament | Biblical New Testament
 sons of Isaac: Esau and Jacob Israel -
sons of Isaac: Esau and Jacob Israel -